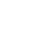As the global economy continues to face significant challenges and uncertainty remains the buzzword of the era, data becomes the new oil for businesses across sectors. In this unpredictable environment, data and analytics can help companies not only manage and mitigate risk but also identify opportunities to adapt and grow.
Moving to data-driven business models – where the decision-making process is based on data rather than intuition – is core to the digital transformation wave that will sweep across every industry in 2024 and beyond. How organisations collect, analyse, manage and use data will be a pivotal factor in shaping the destiny of almost every market segment in the years to come.
.png?width=615&height=297&name=Blog%20Image%20Template%20(12).png)
But in the world of data, there is no standing still. Large volumes of data are generated, collected and consumed at an unprecedented scale. Innovative technologies that offer faster access to data and more reliable insights are constantly emerging, and new trends are revolutionising the business landscape.
Some of the most influential trends driving today's accelerating market include advances in data analytics, big data and data science, innovations related to the cloud, AI, automation, and new data architectures. For organisations of all sizes, embracing these data trends will be crucial for staying competitive as they move through the new year.
In this article, we will break down the top trends predominating the data space today, as well as the future challenges for the data industry.
2023 Overview – Steps Towards the Future
During the pandemic, data and analytics played a key role in forecasting the future for businesses and society. Since then, increasingly more sectors have resulted in analysing and interpreting data as they sought to embrace new ways of working, reach new markets and build business resilience.
The year 2023 saw more exciting developments in the field of data, analytics and AI, which helped shape the way organisations operate. From the emergence of generative AI and machine learning systems to the growth of cloud adoption and data-powered tools, these advancements were a major turning point for many business areas as they began to realise the true potential of data-driven insights and the power of AI to drive innovation.
Today, more data analysts and business leaders are joining forces to improve, simplify, and enhance data use. And as we continue moving into 2024, we can expect even more breakthroughs that will radically transform workflows across various industries and shift the way companies leverage data and analytics to gain a competitive edge.
The Top Data Trends in 2024 and Beyond
Here are the data trends that will transform how businesses are run across the world in 2024 and how organisations can prepare for the future of data, analytics and AI:
1. Increased Data Migration to the Cloud
In past decades, organisations handled their data in their own storage infrastructure, resulting in massive data centres which they had to manage, secure and operate. However, due to the global spike in data volume, increasingly more companies are shifting to the cloud to improve efficiency, reduce expenses, incorporate cutting-edge technologies into their IT infrastructure, and rely on outside services to address security concerns.
Because of these advantages, further data migration to the cloud will remain a key trend in 2024 as businesses seek to become more profitable, agile and innovative in their operations. In addition, as more data continues to move to the cloud and more innovations in cloud storage and processing emerge, organisations are expected to shift towards new data architecture approaches in the coming years to handle the variety, veracity and volume challenges of big data.
- Multi-cloud
According to Forbes, 2024 could be the year businesses understand the advantages of diversifying their services across several cloud providers, including improved flexibility and security. By adopting a multi-cloud infrastructure, companies avoid potentially damaging business models such as building applications and processes exclusively on one cloud platform, such as AWS, Google Cloud, or Microsoft Azure. There are numerous limitations in a single-cloud model, including downtime and privacy concerns, vulnerability to attacks, less control and flexibility in design, limited resources and additional platform dependencies.
As containerised applications become more popular, they can be easily ported across different platforms when service levels change or more cost-effective solutions become available.
- Data Lakes
Rather than centralising data storage in data warehouses that require complex and time-intensive extraction, transformation, and loading processes, enterprises have evolved the data lake concept – which has become one of the most popular repositories used to store data today.
Data lakes store large amounts of structured and unstructured data until needed. The data lake assigns a unique identifier and metadata tags to each piece of data. In this way, data can be accessed more quickly. Unlike most data warehouses and databases, data lakes can also handle a wide range of data types (such as unstructured and semistructured data like images, videos, and audio) for machine learning tasks.
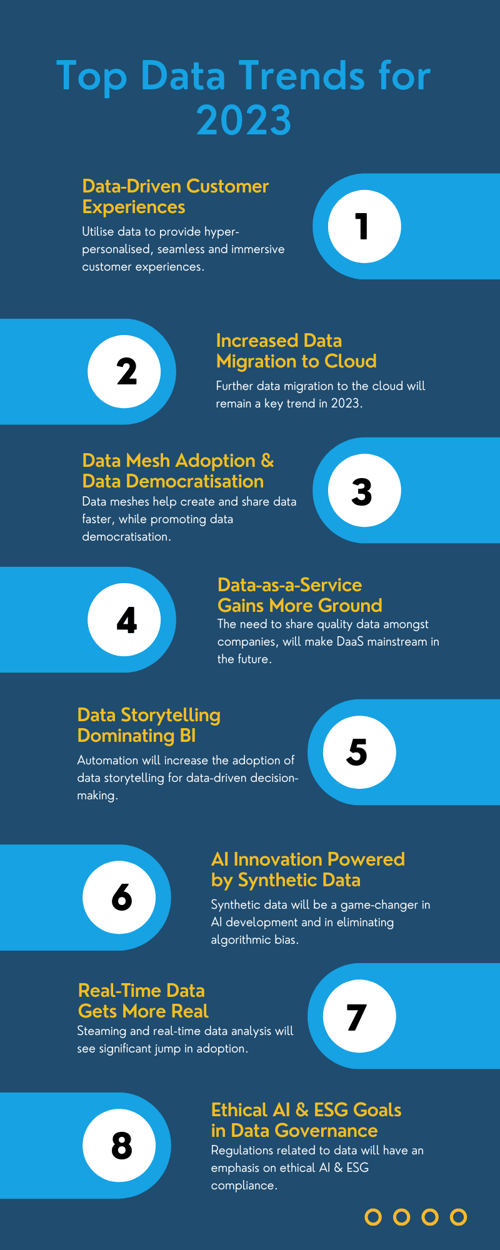
2. Data-Driven Customer Experiences
In the digital age, customer experience (CX) is king – it can make or break a brand. Today, two-thirds of companies compete on customer experience alone. But how do you keep up on delivering superior CX when your top competitors are just one click away? Well, the answer lies in the data.
Data-led customer experience is one of the newest trends in the data sphere today. The concept is that businesses can utilise the data they gather to provide increasingly hyper-personalised, seamless and immersive customer experiences. By analysing and measuring every aspect of customer exchanges, businesses can uncover intelligent insights to understand customer behaviour (what they want, how they want it, and when they want it) and find ways to improve processes or make them more enjoyable. This can translate to more user-friendly software and improved user interface, reduced friction and hassle in online shopping, enhanced customer service, more data transparency, personalised goods and services, and everything in between.
In 2024, many organisations are expected to focus on gathering more data from more areas of the business that will enable them to make better and bolder decisions based on insights, as well as on finding new ways to leverage this data to create personalised and frictionless customer experiences.
3. Data Mesh Adoption and Data Democratisation
Originally proposed by Zhamak Dehghani in 2019, the data mesh concept remains a hot topic, reflecting a different approach to collecting, managing, sharing and reusing data to generate maximum benefit both inside and outside the organisation. But what does data mesh mean, and how does it enable data democratisation?
Data mesh is a data architectural approach that focuses on creating a distributed and decentralised way of dealing with data, making it faster to create and share data products. Unlike other data architectures (such as databases, data warehouses, and data lakes), the data mesh framework treats data as an asset, addresses the challenges of diverse data sources in a human-centred way, and promotes data democratisation by enabling enterprise-wide users to access any dataset across the organisation.
A rapid increase in data mesh adoption is anticipated in 2024 as more and more organisations will be looking for ways to leverage their data better to drive efficiency, transparency, innovation, and new revenues. Moreover, as more organisations implement data meshes, more business lines will come together to share and benefit from each other's data.

4. Data-as-a-Service Gains More Ground
Since the pandemic, the data-as-a-service (DaaS) industry has seen many growth opportunities, especially in the healthcare sector. And as more users have increased access to high-speed internet, it is expected to have a broader reach in the years to come. In fact, according to Technavio, the global DaaS market will increase by $57 billion from 2022 to 2027 at a CAGR of 36.92%.
Enabled by the cloud, DaaS is a software tool used to analyse and manage data which allows companies and users to access, use and share data sources collected by third parties via cloud services on a pay-as-you-go or subscription-based billing model. This model not only allows enterprises to cut costs from building their own expensive, proprietary data collection and storage systems but also makes data sharing easier across departments and industries. This plays a big part in the democratisation of data mentioned above.
As the future of collaboration is expected to expand beyond the business line, the need to share governed data and quality insights with other organisations will transform DaaS into a standard method of managing, storing, analysing, and sharing data in the years to come. Consequently, this will prompt more organisations to build data-as-a-service platforms to market their internal intellectual property to their peers and competitors. Despite the means, this will ultimately lead to a greater level of productivity and collaboration not just within the business but also between sectors.
4. Real-Time Data Gets More Real
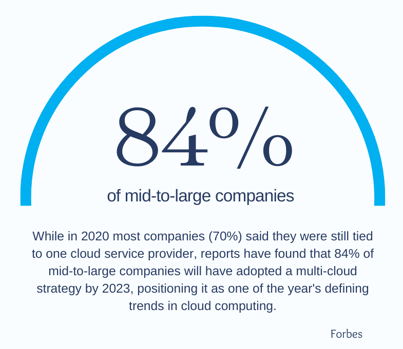
Whether you want to achieve greater customer satisfaction, stay on top of the competition, or improve your products and services, you want to know what is happening in the market, what competitors are doing, and what customers want right now – rather than later. This is why real-time data is increasingly becoming businesses' most valuable source of information.
As data streams grow larger, faster, and more complex by the minute, the speed at which these insights are put into use is becoming just as important as the insights themselves. Besides improving personalisation efforts and the overall customer experience, real-time data can enhance business agility, campaign performance, operational efficiency, as well as customer understanding.
As more organisations realise its potential, the rise of streaming and real-time data reporting and analysis for speedier, data-driven decision-making will see a significant jump in adoption. In 2024, real-time data will go mainstream, and businesses that believe they're already good enough when it comes to real-time tech will fall behind or lose their competitive edge.
Companies that want to work with real-time data and take full advantage of robust streams of the most accurate and up-to-date insights need to establish more sophisticated real-time data analytics infrastructure and strategies. For different businesses and sectors, these strategies may vary from analysing visitor clickstream data to determining what offers and promotions to make available to them in e-commerce to monitoring online transactions in real-time for fraudulent activity in the case of financial services.

6. Data Storytelling Dominating AI
Data storytelling has gained a lot of attention in the past years, and it is here to stay in 2024 – for good reason. Data storytelling comprises data, narrative and visualisations. By blending the precision of numbers with the compelling narrative of a shared vision and a powerful call to action, data and analytics (D&A) leaders can effectively make data stories stand out, gain the decision-makers' attention, and improve how organisations make data-driven decisions.
With the rise of digital business and data-driven decision management, data storytelling has become a skill often associated with data science and business analytics. Today, automated data storytelling is considered by many the future of analytics and is expected to dominate business intelligence (BI) in the next few years. In fact, Gartner predicts that by 2025, data stories will be the most widespread way of consuming analytics and that 75% of stories will be automatically generated using augmented analytics techniques.
While automation will increase the adoption of data storytelling for data-driven decision-making, using automated data stories does not come without risks. Firstly, the issue of keeping the data compelling or relevant can't be solved using algorithms. The human factor retains its primary role in assessing the quality of the data but also the quality of the story. Even though new creative AI techniques have accelerated the content production life cycle and improvements in machine learning techniques (such as deep learning and neural networks) have enabled AI to generate content, humans should remain in the loop during the publishing step.
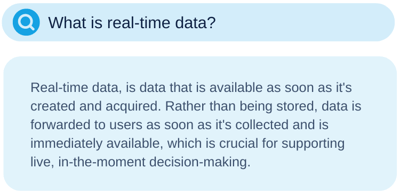
7. AI Innovation Powered by Synthetic Data
The amount of data produced daily is growing exponentially and is expected to reach 175 zettabytes by 2025. This number could give the impression that data is available at an unbelievable scale at everyone's disposal. However, that's not exactly the case. Many artificial intelligence (AI) innovations get stalled due to data scarcity or because data collection is too expensive or time-consuming. In these cases, synthetic data is a good alternative.
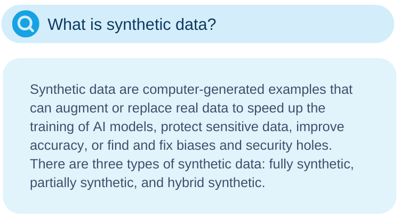
Data synthesis enables AI companies to rapidly augment their existing datasets and simulate scenarios that are difficult to generate in the real world. For example, voice recognition tools can be used in banking to create synthetic financial data to improve fraud detection. Or in automotive, synthetic data tools can use source images to create synthetic variations of car crashes – data that is rare or dangerous to capture in real life.
In 2024, synthetic data is expected to be a game-changer not only in accelerating the development and deployment of AI but also in eliminating algorithmic bias. Another significant challenge in developing AI, apart from the data availability and quality, is getting the right amount of diverse data to train machine learning-based algorithms. These algorithms require massive amounts of data representative of the different people interacting with them and the contexts in which they will be used. Deploying synthetic data tools is key to solving complex data collection challenges and combating algorithmic bias by ensuring diverse datasets.
8. Ethical AI and ESG Goals in Data Governance
In today's digital world, data is the fuel that drives technology and innovation. The increased spike in data use, generation and sharing also means a greater need for regulations that ensure principles of algorithmic transparency, ethical use of data and AI, data privacy and security, fairness and non-discrimination, accountability, and auditability. In 2024, organisations will need to be able to comply with the proposed regulations related to data, with an emphasis on ethical AI and ESG compliance.
- ESG Data
Environmental, Social, and Governance are the three key components that companies use to determine their environmental efficacy and sustainability goals. As ESG regulations continue to evolve, organisations need to get smarter about how they produce and manage the data they use to measure and report on the progress towards their sustainability goals.
Improving the systems and processes for producing ESG data and embedding a joined-up approach to data collection will be critical for companies that seek to gain greater trust from future investors and customers and accelerate their corporate sustainability. With a growing realisation that high-quality, unbiased, and up-to-date ESG data can add significant value for the organisation, using such insights for better decision-making in 2024 will be a common theme in data analytics.
- Ethical AI
Artificial intelligence technology is improving every year, drastically impacting how we live, work and do business. From Google Home and Alexa to automated office tasks and big data analytics, researchers are constantly creating new applications or approaches for enterprises of all sizes to use this revolutionary technology. However, as the technology improves, the conversations around the ethics of AI become louder.
When it comes to ethical AI, a critical issue is how AI algorithms make deductions. As the algorithms don't tend to be transparent, it can be hard to know if their datasets contain any bias taken into account when the system arrives at its conclusion. Since companies across industries are accelerating the usage of AI for their data-based decision-making, regulations such as the proposed EU Artificial Intelligence Act will continue to emerge in 2024, and ethical AI will become more important than ever in the coming years.
Let's sum up.
Data Challenges in 2024
The constantly increasing speed and volume of data being generated and collected, the limited diversity of that data, as well as the need for more accurate and reliable data will be the main challenges for organisations dealing with data this year.
1. Heavy Data Volumes
Businesses are collecting ever-growing amounts of information at an extremely fast rate, and the volume of data being generated is only likely to grow in the coming years. Dealing with such large volumes of data can be a significant challenge for organisations, as it requires the use of scalable and efficient big data technologies capable of storing, processing, and analysing them.
To address this challenge, organisations are increasingly turning to big data platforms for storage, management, cleansing, and analytics, allowing them to extract the insights that their organisations require when they need them.
2. Data Quality, Availability, and Suitability
Finding and collecting accurate, diverse and valuable data is the core of every data project, business plan, or data-driven decision. However, the availability of suitable data is one of any organisation's most significant challenges. Driven by a general fear of missing out on key insights, businesses tend to collect massive amounts of data without modifying it to determine whether it is useful. Unfortunately, this only clogs them with useless data that can lead to poor decision-making with serious consequences for the business.
Ensuring data quality and integrity is therefore critical when dealing with data. This requires the right data architecture, modelling and administration. Introducing a unified data management strategy within the organisation, investing in a robust BI tool, and enabling seamless data sharing between each business unit are some of the best practices for dealing with data quality and data availability issues.
3. Reduced Data Usability and Delays
Reduced data usability presents yet another challenge for utilising structured and unstructured data. Transforming unstructured data (such as scanned documents and social media posts) into a machine-readable format before processing them increases time-to-data, which can cause delays in decision-making. In most cases, however, organisations need to process and analyse high-quality, real-time data to make informed decisions and take timely action. An e-commerce business, for instance, has to analyse customer data in real-time to identify trends and patterns and make targeted customer recommendations.
Organisations must invest in the right technologies and strategies to effectively manage and derive value from data in real-time. For example, automated tools with advanced AI capabilities can simplify unstructured data extraction and processing, providing accurate, real-time, and quality insights. Moreover, turning to newer-generation analytics tools and platforms can also rapidly reduce the time it takes to generate insights, such as in-memory databases and stream processing platforms.
4. Data Security
Data has become the foundation of every business. However, this valuable asset is often exposed to various threats and vulnerabilities. Although customers have become more aware of their privacy rights, and companies make every effort to ensure data security and compliance, cybercrime today has become more sophisticated. No matter where the data is stored or what risks it faces, data security will remain a top concern for modern enterprises in 2024.
To avoid malicious cyber-attacks and unexpected threats, businesses should work cohesively to design and enforce effective data security policies that consider all aspects of the dynamic data security ecosystem. Moreover, they need to reinforce proactive data governance practices by considering all the possible system vulnerabilities.

By understanding these challenges, organisations can better equip themselves to effectively manage and derive value from data in the years ahead.
Driving the Future with Data
In 2024, data will ultimately determine business success. As organisations across sectors rapidly become data-centric, digital dexterity will become mandatory, and data will be the key differentiator. Those who will be able to turn the vast volume of data into actionable insights and take advantage of the data trends discussed in this article will be more agile and prepared to prosper throughout the year and beyond.
Interested in learning more about future data-based challenges and opportunities?
Watch On Demand our Recent Webinar – Data Trends for 2023, here:
Click here to watch the webinar on demand and hear from a world-leading CDO about which data trends will dominate 2023, what are the barriers and opportunities for diversity in data, and what every data specialist needs to know to harness the year ahead.
About Us
Templeton holds a 26-year track record of recruiting thousands of IT professionals around the globe and a vast database filled with potential candidates that suit your needs. Find out more about our multi-award-winning recruitment services.
Discover – 130+ Best Digital Transformation Statistics for 2023 and Beyond